Case 1
A 36 year old female with recent headache and nausea-vomiting sine 2 weeks ago
No specicific history of CVA or nerurological disease
A suspicious vascular lesion was reported in the Brain MRI and referred for brain CT angiography
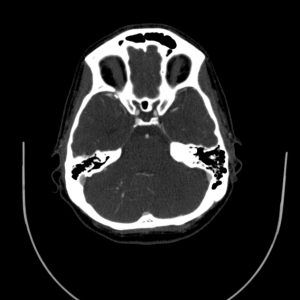
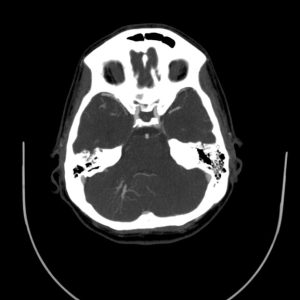
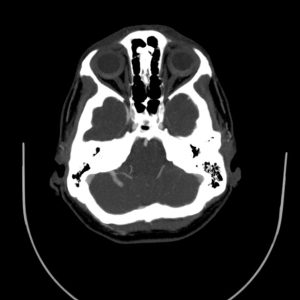
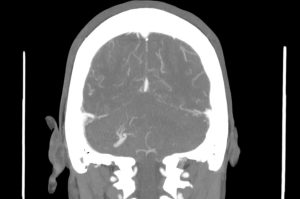
Radiologic findings
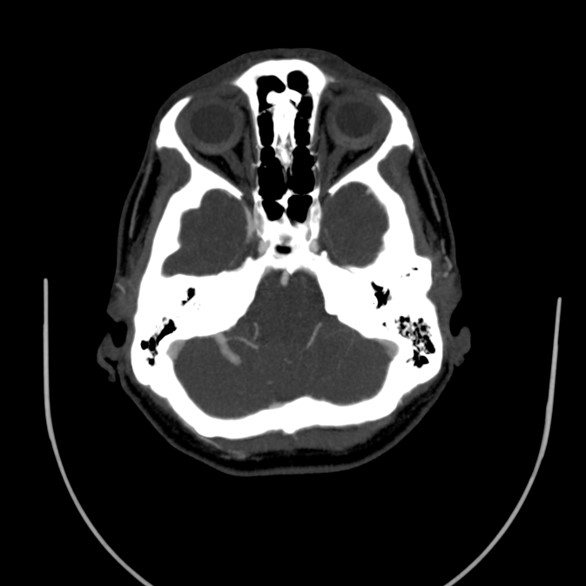
A vascular structure as a network which drains to on vessel
It shows multiple branching appearance in right crebellar hemisphere (Caput Medusa Sign)
Finally the vessel drains to right transverse sinu
No evidence of obvious connection to arterial vessels
No evidence of surrounding hemorrhage
Differential diagnosis
Deep venous anomaly (cerebral venous angioma)
Congenital malformation
Most common verebral vascular malformation
Characterised by multiple veins with appearance of caput medusa or palm tree
draining into a single larger vein which finally drains into a dural sinus or an ependymal vein
Two common types:
frontoparietal region (36-64%) draining towards the frontal horn of the lateral ventricle
cerebellar hemisphere (14-27%) draining towards the ۴th ventricle
Differential diagnosis
arteriovenous malformation
dural sinus thrombosisor or dural arteriovenous fistula with collateral transparenchymal drainage
Sturge-Weber syndrome with leptomeningeal angiomatosis
demyelination may also have enlarged medullary veins
Associations of DVA
Usually solitary (75%)
About 20% (range 8-33%) of cases associated with cavernous malformations
Venous malformations of the head and neck
cortical dysplasia (uncommon)
Case 2
A 60 year old man reffering for chest CT scan with long term history of dyspnea and cough
Symptoms have been exacerbated since 6 months ago
Normal echocardiography and exersise test
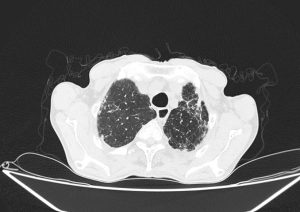
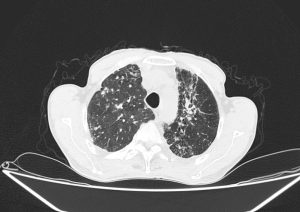
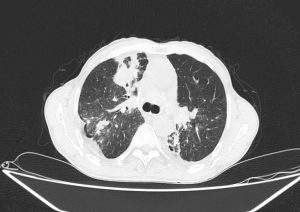
Radiological findings
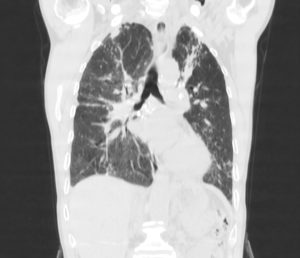
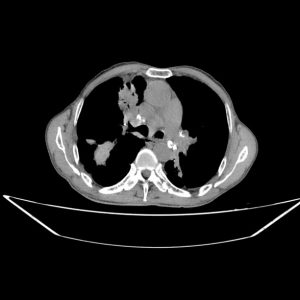
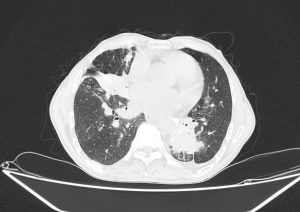
Few hondey combing, diffuse tractional bronchiectasia and irregular interlobular septal thickening in periphery of both lungs
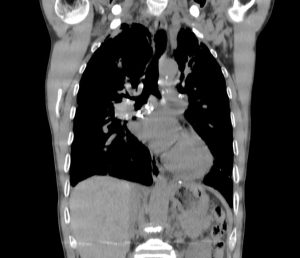
Almost complete collapse of LLL, RML and anterior segment of RUL assocaited with significant narrowing of their airways
Some calcified focci in afformentioned collapses
Small patches of consoliation and ground glass opacities in apeices of both lungs
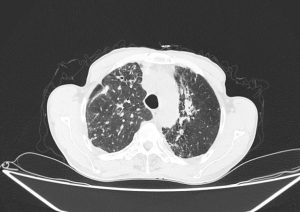
Radiological findings
Scattered centrilobular nodules in both lungs
Bilateral Hillar LAPs containing calcifications
MPA dilation
Few calcified granuloma in liver
Diagnosis
Activation of TB in the backgorund of silicosis as the first diagnosis
History of TB was confirmed
The patient had a history of working in a mine for 3 years
Features of silicosis in CT scan
:Acute
multiple small pulmonary nodules
perilymphatic distribution
upper lobe predominant
accompanied by calcifications
”includes subpleural nodules that coalesce, termed “candle wax” lesions or “pseudoplaques
hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy
calcification of lymph nodes
:Classica complicated silicosis
Soft-tissue masses, often with irregular or ill-defined margins
Calcifications
.Surrounded by areas of emphysematous change
Features of activated TB in CT scan
Multiple areas of consolidation with upper lobe irregular cavity formation
Diffuse extensive bronchiolar infiltration forming a tree in bud appearance elsewhere in the lungs
.axial and coronal MIP clarified this finding in such a nice pattern